Overnight Dexamethasone Suppression Test
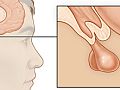
The overnight dexamethasone suppression test checks to see how taking a steroid medicine called dexamethasone changes the levels of the hormone cortisol in the blood. This test checks for a condition in which large amounts of cortisol are produced by the adrenal glands (Cushing's syndrome).
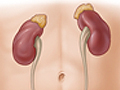
Normally, when the pituitary gland makes less adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), the adrenal glands make less cortisol. Dexamethasone, which is like cortisol, lowers the amount of ACTH released by the pituitary gland. This in turn lowers the amount of cortisol released by the adrenal glands.
After a dose of dexamethasone, cortisol levels often stay very high in people who have Cushing's syndrome. Sometimes other conditions can keep cortisol levels high during this test. Examples include alcohol use disorder, stress, obesity, kidney failure, pregnancy, and uncontrolled diabetes.
The night before the blood test, you will take a dexamethasone pill. The next morning, the cortisol level in your blood will be measured. If your cortisol level stays high, Cushing's syndrome may be the cause.
An ACTH test is sometimes done at the same time as the cortisol test.
Why It Is Done
This test is done to check for Cushing's syndrome. It is a condition in which large amounts of cortisol are produced by the adrenal glands.
How To Prepare
Many medicines can change the results of this test. You may be asked to stop taking some medicines for 24 to 48 hours before your blood is drawn.
How It Is Done
The night before the test (usually at 11:00 p.m.), you will swallow a pill that contains 1 milligram (mg) of dexamethasone. Take the pill with milk or an antacid. This can help prevent an upset stomach or heartburn.
The next morning (usually at 8:00 a.m.), you will have a sample of your blood drawn. A health professional uses a needle to take a blood sample, usually from the arm.
Sometimes a more complete dexamethasone suppression test may be done. For this test, you will take up to 8 pills over 2 days. Then the cortisol levels in your blood and urine will be measured.
How It Feels
When a blood sample is taken, you may feel nothing at all from the needle. Or you might feel a quick sting or pinch.
Risks
There is very little chance of having a problem from this test. When a blood sample is taken, a small bruise may form at the site.
Results
Test results are usually ready in a few days.
An abnormal test result may mean that more tests are needed. A normal test result means that you do not have Cushing's syndrome. This syndrome can be hard to diagnose. So if the test results aren't clear or if they don't help explain your symptoms, you may be referred to see an endocrinologist.
Normal
Each lab has a different range for what's normal. Your lab report should show the range that your lab uses for each test. The normal range is just a guide. Your doctor will also look at your results based on your age, health, and other factors. A value that isn't in the normal range may still be normal for you.
High values
High cortisol levels may be caused by:
- Cushing's syndrome.
- Other health problems. Examples include heart attack or heart failure, fever, poor diet, an overactive thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism), depression, anorexia nervosa, uncontrolled diabetes, and alcohol use disorder.
Related Information
Credits
Current as of: September 25, 2025
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Current as of: September 25, 2025
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.